COVID-19 significantly impacted global health, prompting an urgent need for effective antiviral treatments. Our research aimed to accelerate drug discovery by utilizing computational approaches to identify inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2’s 3CLpro enzyme, crucial for viral replication.
Understanding QSAR and Molecular Fingerprints
Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) modeling predicts biological activity based on chemical structure. Our study uniquely focused on molecular-fingerprint-based QSAR models using augmented Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES), enabling effective data expansion and improved model accuracy.
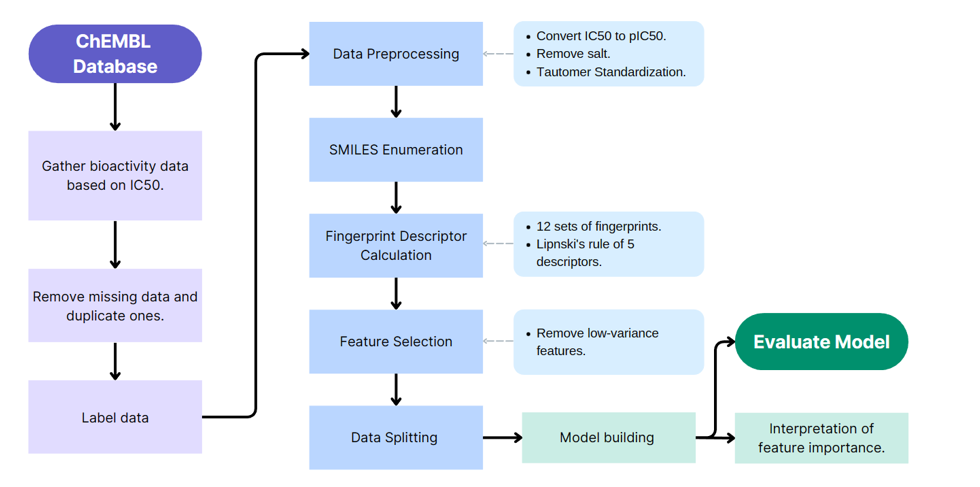
Workflow
Data Acquisition and Enhancement
Initially, data for 198 compounds was obtained from the ChEMBL database. To address dataset imbalance, we employed SMILES enumeration—generating multiple structural representations per compound—to significantly expand the dataset. After augmentation, the dataset comprised 720 inactive and 701 active molecules, greatly enhancing model training and accuracy.
Model Development and Evaluation
We tested six machine learning algorithms with twelve fingerprint descriptor methods to build robust predictive QSAR models. Random Forest consistently outperformed others, showing accuracy and precision scores above 90%. Among fingerprinting techniques, the Substructure Count descriptor emerged most efficient, providing high accuracy (90.15%) with minimal computational complexity.
Key Findings and Feature Importance
Our analysis identified critical molecular features essential for 3CLpro inhibitor activity. Specifically, features like Quaternary mixed ammonium, Tertiary mixed amine, and Primary aromatic amine demonstrated high importance, guiding future experimental validations.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The outcomes highlight computational QSAR as a powerful tool in drug discovery, significantly reducing costs and enhancing research efficiency. Continued refinement with larger datasets could further advance predictive capabilities and hasten therapeutic breakthroughs against COVID-19.
This post provides a high-level overview of the project, covering key aspects and insights. It does not go in-depth but gives a general idea—how it was built and what it does. If you’re curious about the details, feel free to explore the code or reach out!